May 28th, 2024
Exploring Nominal Variable Association
By Zach Fickenworth · 7 min read

Overview
In the world of statistical analysis, understanding the relationships between categorical, or nominal, variables is crucial, especially in social sciences. Nominal variable association delves into the statistical relationships between variables that have no inherent ranking, such as gender, race, or college major. This blog will explore the methods used to analyze these relationships, particularly focusing on crosstabulation and Chi-Square tests, and how tools like Julius can enhance this analytical process.
What is Nominal Variable Association?
Crosstabulation: A Primary Tool for Analysis
Crosstabulation, or contingency table analysis, is a common method used to examine relationships between nominal variables. It involves tabulating the frequencies of one variable against another, allowing researchers to observe if being in one category of a variable is likely to relate to being in a certain category of another variable.
Example Questions:
- Is there an association between music genre selection and venue type?
Using crosstabulation, researchers can compare observed frequencies in the table to expected frequencies, providing insights into patterns of association between variables like race and college major.
Chi-Square Test of Independence
Measures of Association Strength
1. Contingency Coefficient (CC): Ranges from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating a stronger association. However, it's sensitive to table size and should be interpreted cautiously.
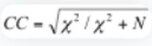
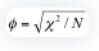
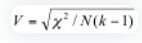
Interpreting Association Strength
- Less than .10 indicates a weak association.
- Between .11 and .30 suggests a moderate association.
- Greater than .31 signifies a strong association.
Assumptions in Nominal Variable Association
- Variables must be categorical.
- Presence of a zero in crosstabulation may hinder the assessment of association.
How Julius Can Assist
Julius, an advanced statistical tool, can significantly aid in the analysis of nominal variable associations:
- Automated Crosstabulation: Julius can quickly generate crosstabulation tables, saving time and reducing manual errors.
- Chi-Square Test Computation: It can perform Chi-Square tests efficiently, providing accurate assessments of associations.
- Measures of Association: Julius offers calculations of CC, Phi Coefficient, Cramer’s V, and Lambda, including directional measures for Lambda.
- Data Interpretation: It provides clear interpretations of these statistical measures, helping researchers understand the strength and nature of associations.
- Visualization Tools: Julius can create visual representations of crosstabulation results, making it easier to identify and communicate patterns in the data.
